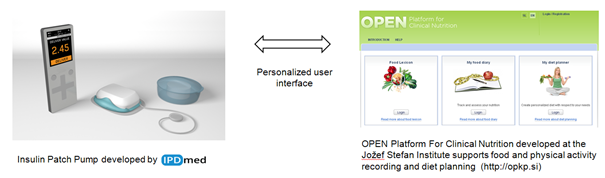
“Computing machines can do readily, well, and rapidly many things that are difficult or impossible for men and men can do readily and well, though not rapidly, many things that are difficult or impossible for computers. This suggests that a symbiotic cooperation, if successful in integrating the positive characteristics of men and computers, would be of great value” (Licklider, 1960).
In 1960, Licklider identified the problems for realization of such ‘man-computer symbiosis’ in speed mismatch between men and computer, memory hardware requirements, memory organization requirements, differences between human and computer language and input and output equipment, the latest being the most problematic.
Fifty years later this still holds true.

Word cloud based on this post about NUIs. The most emphasized
word, ‘skills’ highlights the importance of making NUIs feel intuitive to use, which can
be achieved by designing the interface so that it relies on skills that users already possess
Today Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) is concerned with the above-mentioned problems i.e. the design, evaluation and implementation of interactive computing systems for human use and the study of major phenomena surrounding them (Hewett et al., 2009). HCI is an interdisciplinary area deriving its knowledge from computer science (application design and engineering of human interfaces), psychology (the application of theories of cognitive processes and the empirical analysis of user behaviour), sociology and anthropology (interactions between technology, work, and organization), and industrial design (interactive products).
Interaction between human and computers takes place at the user interface. This is why research and development of user interfaces lies at the very core of HCI. We will first briefly present the development that led to today’s user interfaces and then focus on multitouch displays, their construction and use cases.
From Punch Cards to Natural User Interfaces
Early digital computers used batch interfaces. They consist of punch cards for programs and data input and prints as output. Batch interfaces are non-interactive, which means that the user has to specify everything prior to processing and is never prompted for additional input until the job is done. With the connection of teletype machines to computers and the advent of dedicated text-based CRT terminals in the late 50s, batch interfaces gave space to command line interfaces (CLI). CLIs brought speed and interactivity to human computer interaction. In the early 60s, Douglas Engelbart invented the first mouse prototype used for manipulating text-based hyper-links as a part of his ‘augmenting human intellect’ project (Engelbart, 1962). Later, researchers at Xerox PARC extended the concept of hyper-links to graphics and by doing so created the first graphical user interface (GUI). In respect to the CLI, GUI facilitates a more intuitive interaction because there is no need to learn commands by heart as available commands are presented on the screen in the form of windows, icons, menus and a pointer. This interaction paradigm can be emphasized by the acronym WIMP. Further efforts focused on the development of interfaces that interact with humans in a seamless way by understanding natural expressions of the user’s intent instead of forcing him/her to learn new rules for interaction. The results of these efforts are, among others, various speech and gesture recognition techniques known as Natural User Interfaces or NUIs.
Natural User Interfaces
NUI Group, a global research community focused on the open discovery of natural user interfaces, defines natural user interfaces as an emerging computer interaction methodology which focuses on human abilities such as touch, vision, voice, motion and higher cognitive functions such as expression, perception and recall. A natural user interface seeks to harness the power of a much wider breadth of communication modalities which leverage skills people gain through traditional physical interaction (NUI Group Community, 2009). Some representative examples of such interfaces are:
- Multitouch displays (Han, 2005): tracking and recognizing multiple fingers (and objects) on a display, which leads to new interaction techniques. These displays differ from touchscreens capable of detecting one touch in that they allow for a different interaction paradigm, while touchscreens are just a replacement for the input device, usually the mouse, in a GUI.
- Speech recognition (Rosenfeld et al., 2000): interfaces based on speech recognition, speech synthesis and natural language processing.
- Space gesture recognition (Hay et al., 2008): 3D tracking or motion capture using Nintendo Wii or similar controllers as stereo vision systems. The user interacts with the system by performing, usually predefined, spatial gestures.
- Interfaces based on electrophysiological signals (e.g. Brain-Computer Interfaces, Wolpaw (2002)): these interfaces determine the intent of the user from electrophysiological signals caused by brain, muscle, and cerebral cortex activity. For example, classifying finger gestures by interpreting forearm electromyography (EMG) signals caused by muscle movements (Saponas et al., 2009). These interfaces are also known as direct neural interfaces, mind-machine interfaces or brain-machine interfaces.
The main property of these interfaces is their intuitiveness. Ideally, a natural user interface does not require the user to undergo any training in order to interact with it. In other words, NUIs excel in terms of learnability and discoverability. NUIs build on the knowledge users get in their everyday life and exploit interaction metaphors with real-world objects to interact with digital objects in the digital world. The actual definition of NUIs is subject of ongoing debate and there are many definitions available. Some of the more concise definitions are:
- TechTarget: “A natural user interface (NUI) is a system for human-computer interaction that the user operates through intuitive actions related to natural, everyday human behaviour … A NUI may be operated in a number of different ways, depending on the purpose and user requirements. Some NUIs rely on intermediary devices for interaction but more advanced NUIs are either invisible to the user or so unobtrusive that they quickly seem invisible.”
- TechTerms: “A NUI is a type of user interface that is designed to feel as natural as possible to the user. The goal of a NUI is to create seamless interaction between the human and machine, making the interface itself seem to disappear.”
- Wikipedia, Ron George: “…a user interface that is effectively invisible, or becomes invisible with successive learned interactions, to its users.”
Some authors offer a more lengthy definition of natural user interfaces or give a short definition accompanied by a lengthier explanation, like Joshua Blake’s definition of NUIs:
“A natural user interface is a user interface designed to reuse existing skills for interacting directly with content (Blake, 2013).”
He explains his definition as follows:
“NUIs are designed. First, this definition tells us that natural user interfaces are designed, which means they require forethought and specific planning efforts in advance. Special care is required to make sure NUI interactions are appropriate for the user, the content, and the context. Nothing about NUIs should be thrown together or assembled haphazardly. We should acknowledge the role that designers have to play in creating NUI style interactions and make sure that the design process is given just as much priority as development;
NUIs reuse existing skills. Second, the phrase ‘reuse existing skills’ helps us focus on how to create interfaces that are natural. Your users are experts in many skills that they have gained just because they are human. They have been practicing for years skills for human-human communication, both verbal and non-verbal, and human-environmental interaction. Computing power and input technology has progressed to a point where we can take advantage of these existing non-computing skills. NUIs do this by letting users interact with computers using intuitive actions such as touching, gesturing, and talking and presenting interfaces that users can understand primarily through metaphors that draw from real-world experiences. This is in contrast to GUI, which uses artificial interface elements such as windows, menus, and icons for output and pointing device such as a mouse for input, or the CLI, which is described as having text output and text input using a keyboard. At first glance, the primary difference between these definitions is the input modality – keyboard versus mouse versus touch. There is another subtle yet important difference: CLI and GUI are defined explicitly in terms of the input device, while NUI is defined in terms of the interaction style. Any type of interface technology can be used with NUI as long as the style of interaction focuses on reusing existing skills;
NUIs have direct interaction with content. Finally, think again about GUI, which by definition uses windows, menus, and icons as the primary interface elements. In contrast, the phrase ‘interacting directly with content’ tells us that the focus of the interactions is on the content and directly interacting with it. This doesn’t mean that the interface cannot have controls such as buttons or checkboxes when necessary. It only means that the controls should be secondary to the content, and direct manipulation of the content should be the primary interaction method.”
In his keynote speech at Interact 2011, Antão Almada emphasizes Blake’s ‘interaction style over input modality’ point of view: “People feel naturally what they are supposed to do. Natural means ease of use, non-invasive sensors, to simplify as much as possible, to give intelligence to the interface so that the users get only the useful information.” The company he works for uses NUIs mainly in marketing applications, where people do not have time to learn how to interact with the applications they build and the need for easy, learnable interaction based on skills people already have is particularly strong.
Richard Monson-Haefel’s presents yet another variant of NUI definition: “A Natural User Interface is a human-computer interface that models interactions between people and the natural environment.” He continues specifying a couple of aspects of this definition that are especially important:
“NUI is a form of HCI. It is important that we make that explicit;
NUI models natural interactions. That means it leverages and uses as a template the interactions people have with each other (e.g. speech and gestures); NUI also models interactions between people and the natural environment (e.g. water and rocks) as opposed to their artificial environment (e.g. computers and cars.).”
Dennis Wixon talks about NUIs and interfaces in general in terms of principals and guidelines (Wixon, 2008). He believes that from a historical analysis of user interfaces we can extract a set of principles and guidelines for each interface type. “The principles are what drives the design. The guidelines are simply derivations of the principles for an individual context. Principles are what’s important. Principles and data drive successful design.” In this sense he analyses three different interface types that primarily build upon text—command line interfaces, graphics—graphical user interfaces and objects—natural user interfaces. He notes that interaction in CLIs builds upon the psychological function of recall as the user is disconnected from the static system he interacts with and has to direct the system by learning/recalling a high number of commands. He continues by describing GUIs as an exploratory and responsive type of interaction, where the user scans through menus and recognizes the commands he had to learn and recall within CLIs. Wixon argues that interaction with GUIs is indirect as the user actually controls the mouse or the keyboard and not the GUI itself. NUIs, on the other hand, provide an unmediated interaction that is evocative and thus relies on user intuition. The commands in a NUI are few and the interaction is fast. Wixon states that NUIs are also contextual and that they understand the environment they are in and react to it naturally. He concludes this analysis of interfaces by extracting a set of principles that should apply to NUI design: the principal of performance aesthetics (the interaction should be enjoyable), the principle of direct manipulation, the principle of scaffolding (the system should support actions as you move forward and should reveal itself in those actions), the principle of contextual environments and the principal or the super real (to take real things and extend them in a logical yet unrealistic way in the digital world). These 5 principles build upon three core principles: social, seamless, spatial. These are explained on an example – the Microsoft Surface multitouch tabletop computer. Surface is social as it encourages social interaction around a shared information space and brings people together instead of isolating them, the actions of a Surface user and the interaction with the Surface are the same, which makes the Surface seamless and spatial as the objects in the interface have an implied physicality and the interaction with the Surface leverages spatial memory.
Wixon co-authored a book about NUIs with Daniel Wigdor, called ‘Brave NUI world’ (Wigdor and Wixon, 2011). The book presents guidelines stemming from the abovementioned principles and tries to define NUIs from a user centred perspective: “The word ‘natural’ in natural user interfaces describes the user’s feelings during interaction and not the interface itself. Interfaces often cited as NUIs, e.g. multitouch displays with their highbandwidth input modality, are not natural per se – they instead provide a higher potential for developing a natural user interface, if and only if an all-new interface is designed with new input actions, new affordances – in short, a new paradigm.” In their view, creating a natural user interface is a design goal. It can be achieved through “a clear viewpoint, hard work, careful design, rigorous testing and some luck.” The clear viewpoint here is their vision of natural user interfaces: “Our vision is that a natural user interface is one that provides a clear and enjoyable path to unreflective expertise in its use. It makes skilled behaviour seem natural in both learning and expert practice. It makes learning enjoyable and eliminates the drudgery that distracts from skilled practice. It can make you a skilled practitioner who enjoys what you are doing. Natural in this sense does not mean raw, primitive, or dumbed down.” Finally, they summarize their definition of natural user interfaces as follows:
“A NUI is not a natural user interface, but rather an interface that makes your user act and feel like a natural. An easy way of remembering this is to change the way you say ‘natural user interface’ – it’s not a natural user interface, but rather a natural user interface.”
Bill Buxton supports this natural user interface over natural user interface point of view: “It’s not about speech, it’s not about gesture, it’s not even about the phone, and it’s not about human-to-human communication,” he says. “How these things work together in a natural and seamless way that reduces complexity for the users — that’s what we’re about. Getting these things right opens up another dimension in how we have technology integrated into our lives” (Buxton, 2010). His understanding of what natural in natural user interfaces means is: “designing to take advantage of the skills we acquired in a lifetime of living in the real world. These skills are motor-sensor skills, cognitive skills and social skills.” In this sense, a designer of natural user interfaces must take care not to waste people’s skills. This design paradigm also leads to interfaces that are natural to some users and not natural to others. For example, someone that has invested the time and effort to learn touch typing may find editing text in ‘vi’ natural. On the other hand, despite touch being usually regarded as a natural means for interaction, Foehrenbach et al. (2008) surprisingly report how tactile feedback added to gestural interaction with high resolution interactive walls increases error rates by 10 %. Kurfess (2013) shares this hardware-agnostic point of view on NUIs. In his opinion, natural user interfaces are not about input modalities, but about interaction style. A user interface becomes natural with careful interaction design and planning; the word natural here means that interaction is appropriate for the user, the content, and the context in which the interaction takes place. This can be achieved by reusing skills that the user already has and building upon experience and expertise often unrelated to computer use. Kurfesses key guidelines for developing natural user interfaces are the use of direct manipulation where possible, enabling instant expertise for the user, reducing cognitive load and inducing progressive learning.
The roots of this debate about the essence of natural interaction can be traced back to the late 70s, and early 80’s. Although at the time the expression natural user interfaces was not yet born, Ben Shneidermann’s work on direct manipulation belongs in this context. In (Frohlich, 1993) Frohlich et al. summarized direct manipulation as “a style of interaction characterized by the following three properties:
- Continuous representation of the object of interest,
- Physical actions or labelled button presses instead of complex syntax, and
- Rapid incremental reversible operations whose impact on the object of interest is immediately visible.”
The benefits of direct manipulation are “ease of learning, ease of use, retention of learning, reduction and ease of error correction, reduction of anxiety and greater system comprehension” ( Shneiderman (1982), p. 253). Due to the overlapping of these benefits and the various definitions of natural user interfaces and their goals we can say that findings related to direct manipulation can be applied to NUIs as well. In 1985, Hutchins et al. (1985) deconstruct the term directness in direct manipulation in two parts: the psychological distance between user goals and the action a specific interface requires to achieve these goals, and to psychological engagement of feeling oneself to be controlling the computer directly rather than through some intermediary. “Essentially distance refers to the mismatch between the way a user normally thinks about a problem domain and the way it is represented by a computer. Systems which reduce distance reduce this mismatch and the associated mental effort of working out what can be done in the system (semantic distance) and how to do it (articulatory distance). Engagement, on the other hand, refers to a particular style of representation based on a model world metaphor rather than on a conversational metaphor for interaction. Systems can encourage a feeling of engagement by depicting objects of interest graphically and allowing users to manipulate them physically rather than by instruction.”( Frohlich (1993), p. 3) NUIs’ strategy to reduce the above-mentioned psychological distance between user goals and action is to exploit skills users already possess. It is this ‘recycling/remixing/reusing of skills’ that makes NUIs intuitive. However, a lower distance between goals and actions is not always good – to accomplish more abstract tasks, this distance is actually beneficial, for example: repetitive tasks are easier to accomplish within a command line interface with a ‘for loop’ than manually in a more direct user interface. In this sense, Hutchins et al. conclude that direct manipulation systems benefit from the simplified mapping between goals and actions needed in an interface to achieve those goals, but at the same time lose some expressive power due to the loss in abstraction corresponding to the simplified mapping. As Bill Buxton often puts it: “Everything is best for something and worst for something else.” Therefore in 1993 Frolich (Frohlich, 1993) proposed a shift in interaction from directness to gracefulness: “The puzzle of desirable indirectness in interaction is solved if we shift to a more social definition of directness as interaction in which there is least collaborative effort expended to achieve a users’ goals. Activities which are cognitively indirect can then be seen as socially direct in that they have the effect of minimizing the joint work carried out by system and user entailed in achieving task success.” Frolich’s notion of graceful interaction builds upon Hayes’ and Reddy’s (Hayes and Reddy, 1983), who in 1983 proposed a decomposition of the term graceful interaction into a set of skills: “skills involved in parsing elliptical, fragmented, and otherwise ungrammatical input; in ensuring robust communication; in explaining abilities and limitations, actions and the motives behind them; in keeping track of the focus of attention of a dialogue; in identifying things from descriptions, even if ambiguous or unsatisfiable; and in describing things in terms appropriate for the context.” We can say that graceful interaction addresses some of the generally acknowledged problems of NUIs. Don Norman in (Norman, 2010) argues that a pure gestural system makes it difficult to discover the set of possibilities and the precise dynamics of execution that an interface requires: “It is also unlikely that complex systems could be controlled solely by body gestures because the subtleties of action are too complex to be handled by actions – it is as if our spoken language consisted solely of verbs. We need ways of specifying scope, range, temporal order, and conditional dependencies. As a result, most complex systems for gesture also provide switches, hand-held devices, gloves, spoken command languages, or even good old-fashioned keyboards to add more specificity and precision to the commands. Gestural systems are no different from any other form of interaction. They need to follow the basic rules of interaction design, which means welldefined modes of expression, a clear conceptual model of the way they interact with the system, their consequences, and means of navigating unintended consequences.” He continues: “Whether it is speech, gesture, or the tapping of the body’s electrical signals for ‘thought control,’ all have great potential for enhancing our interactions, especially where the traditional methods are inappropriate or inconvenient. But they are not a panacea.”
If direct and graceful manipulation have been terms used to discuss NUI-like interaction in the past, some authors suggest new terms for future discussion. Among them are Oviatt and Cohen’s Perceptual User Interfaces (PUI) (Oviatt and Cohen, 2000), Wixon’s Organic User Interfaces (OUI) (Wixon, 2008) and Petersen and Stricker’s Continuous Natural User Interfaces (CNUI) (Petersen and Stricker, 2009). These are often restatements or combinations of other established and NUI related research fields we discussed here. For example, perceptual user interfaces are a combination of natural user interfaces and intelligent user interfaces: “PUIs are characterized by interaction techniques that combine an understanding of natural human capabilities (particularly communication, motor, cognitive, and perceptual skills) with computer I/O devices and machine perception and reasoning. They seek to make the user interface more natural and compelling by taking advantage of the ways in which people naturally interact with each other and with the world — both verbally and non-verbally” (Oviatt and Cohen, 2000).
To sum up …
We can say that all the presented definitions generally agree that natural user interfaces should not revolve around the interface itself but should be focused on how a user perceives the interface. A concise and in this sense correct definition would be:
“Natural User Interfaces are interfaces that are intuitive to use.”
The word cloud presented in the figure above concurs with this definition. We created the word cloud with the text of this section, which surveys various definitions of NUIs. After stop words removal1 , the emphasis of each word is proportional to its normalized frequency in the text. We can see that the word, which strikes out the most, is ‘skills’; for an interface to feel natural it must be intuitive and therefore it must rely on skills that the user has already obtained in life. For example, due to their widespread use, the keyboard and mouse may also be considered as natural user interfaces. In this sense we can say, that once the skills to operate an interface are acquired, any interface can be regarded as natural. To some people, the gesture of waving on a sidewalk (to stop a taxi) is an example of a natural user interface, while to some it is not. It depends on the user, but also on the context in which the interaction takes place. Exploiting contextual information to the benefit of human-computer interaction broadens the communication channel between user and computer even further which in turn opens up new possibilities for designing interaction that exploits skills that users already possess. On one hand, natural user interfaces ease the acquisition, understanding and exploitation of context and on the other hand, context makes achieving natural interaction easier.
Excerpt from the PhD thesis available here.
 Loading...
Loading...
 Loading...
Loading...